

Date: 04 Jun 2025
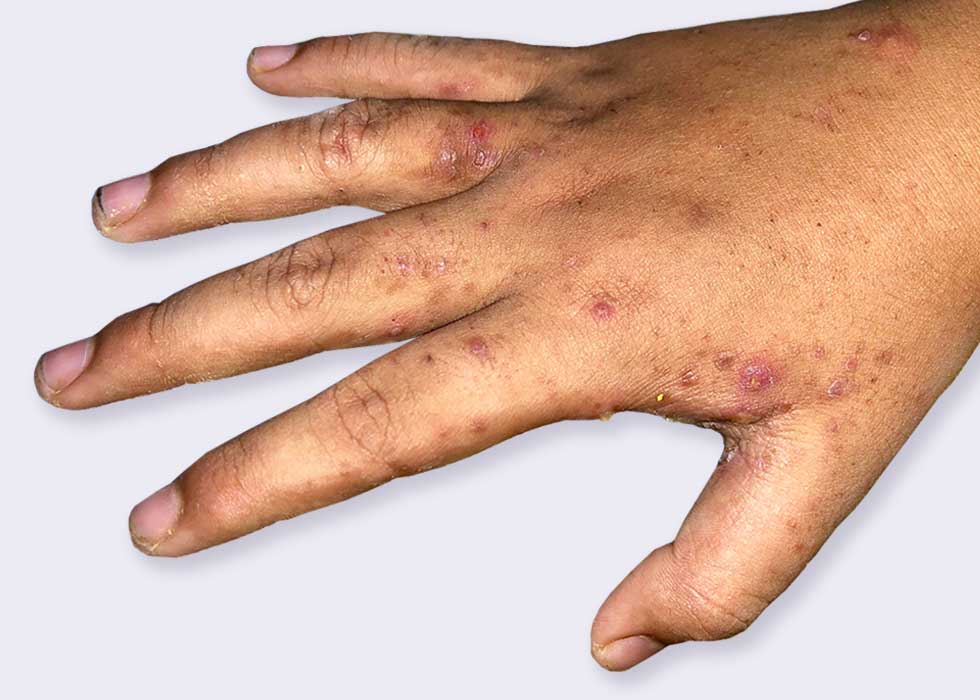
Scabies is a common, intensely itchy skin condition caused by a microscopic parasite known as the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These tiny mites burrow into the skin, laying eggs and causing a persistent allergic reaction that leads to severe itching and skin rashes. Though scabies is not life-threatening, it can cause immense discomfort, sleep disturbances, and social distress if left untreated. Fortunately, it is entirely treatable with the right approach.
At Pharmily, we provide trusted treatment solutions for scabies, including Lindane Cream, to help you manage and recover from this condition effectively.
Scabies is caused by the infestation of the skin by the female scabies mite, which burrows into the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) to live and lay eggs. The body reacts to the presence of the mites, their eggs, and their waste products, which causes an allergic response characterized by itching and inflammation.
Scabies is highly contagious and spreads through:
It is important to note that scabies cannot be transmitted by casual contact, such as a handshake or a brief hug.
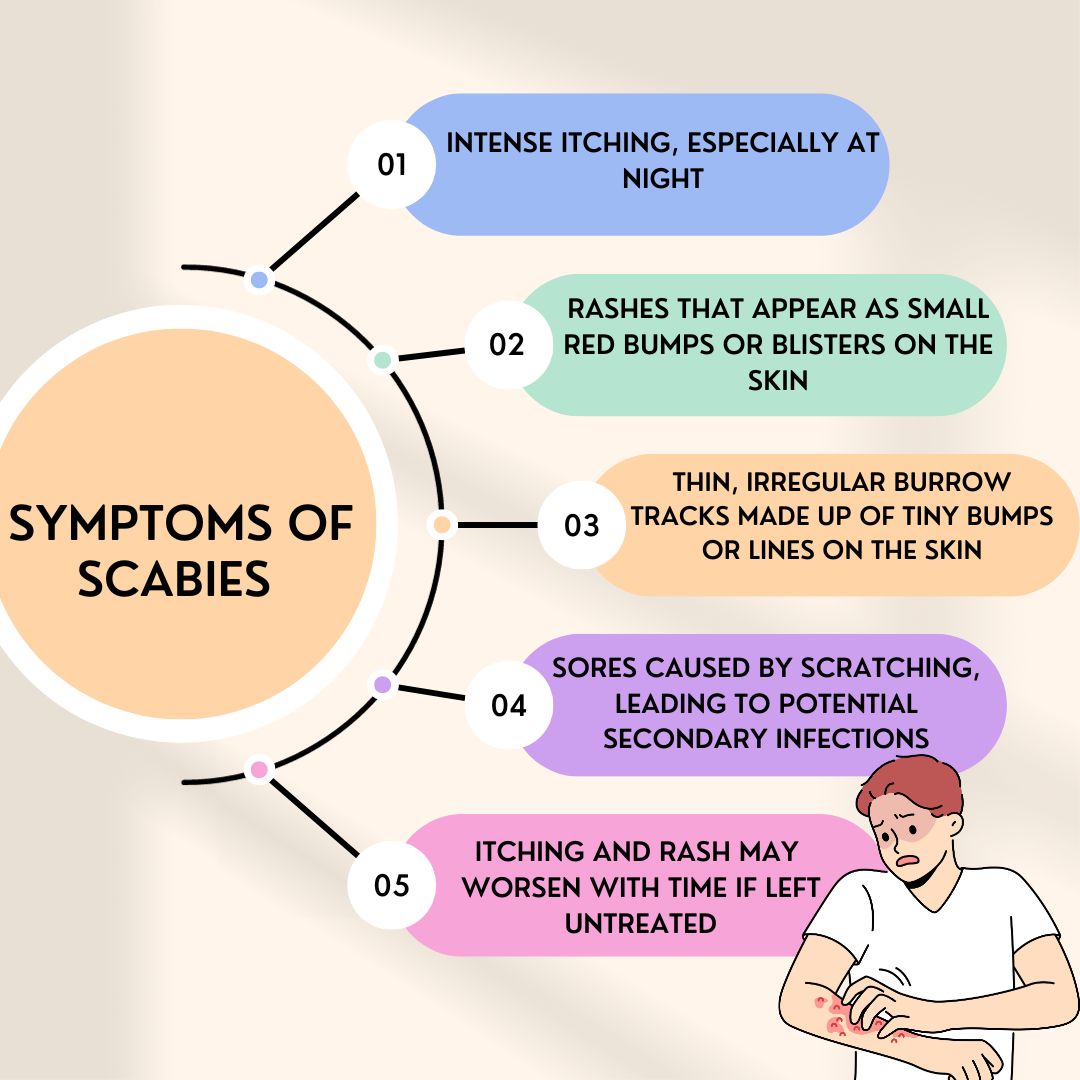
Symptoms of scabies usually develop 2–6 weeks after the initial infestation in individuals who have never been exposed before. In those who have had scabies before, symptoms may appear within 1–4 days due to prior sensitization.
If left untreated, the number of mites on the body can multiply quickly, leading to a more severe form known as crusted scabies (formerly called Norwegian scabies), which is highly infectious and often seen in immunocompromised individuals.
Diagnosis is primarily based on a clinical examination of symptoms and rash patterns. In some cases, a skin scraping may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of mites, eggs, or mite feces.

Successful treatment of scabies requires a combination of topical or oral medications, personal hygiene practices, and the simultaneous treatment of all household members and close contacts to prevent reinfestation.
These are applied directly to the skin and are the first line of defense:
You can order Lindane Cream conveniently from Pharmily, your trusted online pharmacy in Kenya.
You can order Permethrin Cream 5% conveniently from Pharmily, your trusted online pharmacy in Kenya.
Even after successful treatment, itching can persist for several weeks due to the body’s continued allergic reaction to the dead mites. This does not mean the treatment failed.
To manage post-treatment symptoms:
Proper environmental hygiene is crucial in managing scabies. Here’s how you can prevent reinfection:
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of scabies, early treatment is essential. Pharmily offers quality-assured medications, including Lindane Cream, and delivers directly to your home for privacy and convenience.
No. Scabies does not go away without treatment. The mites will continue to reproduce and spread on the body and to others. Without proper medication like Lindane Cream or permethrin, the condition can worsen and lead to secondary infections or crusted scabies in severe cases.
The mites usually die within 24–48 hours of treatment, but itching can persist for up to 2–4 weeks as the body continues to react to dead mites and their waste. This is normal and can be managed with antihistamines or topical creams. If itching continues beyond 4 weeks or worsens, consult a healthcare provider for reassessment.
Lindane Cream is effective but should be used with caution. It is not recommended for infants, pregnant or breastfeeding women, or individuals with conditions like eczema or seizure disorders due to the risk of absorption and potential neurotoxicity. Always follow a healthcare provider’s instructions when using Lindane.
Yes. All close contacts and household members should be treated at the same time, even if they do not show symptoms. Scabies mites can live on the skin for weeks before symptoms appear, so untreated individuals can continue spreading the infestation.
Yes. Reinfestation can occur if proper precautions aren’t taken—such as treating all contacts, cleaning bedding and clothing, and avoiding close contact until treatment is complete. If you are exposed to an infested person again, you can develop scabies once more, even after successful treatment.