

Date: 05 Jun 2025
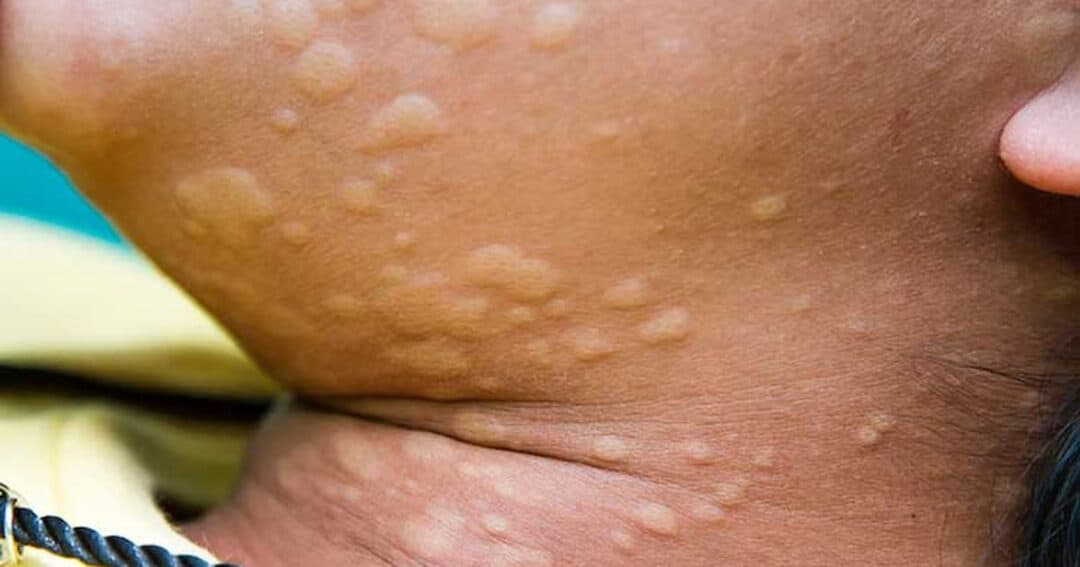
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition marked by red, itchy, and swollen welts that appear suddenly. It can affect anyone and may be triggered by allergic reactions, stress, medications, infections, or environmental factors. Urticaria can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (persisting longer than six weeks). Understanding the root causes and treatment options is essential for effective management and relief.
Urticaria develops when the immune system releases histamine in response to certain triggers. These include:
In some cases, the exact cause remains unknown, especially in chronic urticaria.
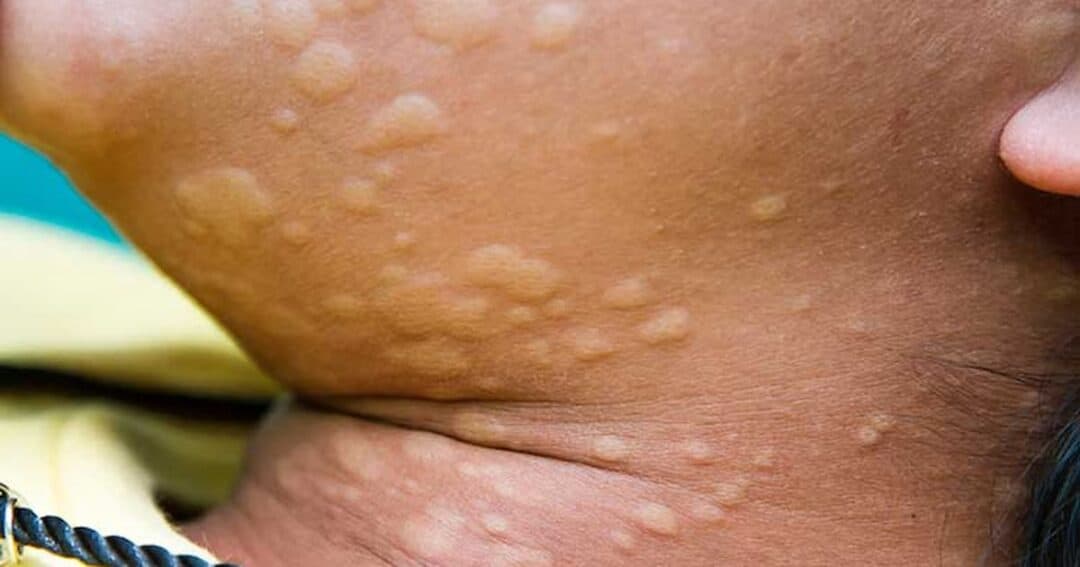
The most identifiable symptoms of urticaria include:
These welts may appear and disappear within hours, but new ones can emerge, leading to prolonged discomfort.
Diagnosis is primarily based on physical examination and a review of the patient’s history. Doctors may ask about:
In chronic cases, blood tests, allergy tests, or skin biopsies may be required.
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing further flare-ups. Mild cases often resolve without medication, but persistent or severe urticaria may require:
Pharmily.co.ke provides a variety of effective treatments for urticaria. Below are trusted products available for convenient online purchase in Kenya:
Cetirizine is a fast-acting, non-drowsy antihistamine ideal for relieving itching, swelling, and redness associated with hives. It works by blocking histamine receptors and is suitable for both acute and chronic urticaria. Its 24-hour effectiveness allows for once-daily dosing and long-lasting comfort.
Calamine lotion is a soothing topical treatment that provides immediate relief from itching and irritation. It cools the skin and helps dry out any weeping welts, making it a useful addition to oral antihistamines for symptomatic relief.
Menthol creams deliver a cooling sensation to the skin, which helps to distract from the discomfort of itching and inflammation. These creams can be applied directly to affected areas and are particularly helpful for nighttime relief when symptoms tend to worsen.
All products are available on Pharmily.co.ke, with options for delivery across Kenya and pharmacist support for personalized care.
Seek medical attention if:
Chronic or severe urticaria may require prescription medications and further investigation.
Preventing urticaria involves identifying and avoiding triggers. Helpful tips include:
No. Urticaria is not contagious. It results from your body’s immune response to a trigger and cannot be spread from one person to another.
In many cases, acute urticaria resolves on its own. Chronic urticaria may persist for months or years but can often be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and medication.
Common food triggers include shellfish, nuts, eggs, dairy, and food additives like sulfites or preservatives. Keeping a food diary may help identify specific culprits.
Acute urticaria can last from a few hours to several days. Chronic urticaria is defined as symptoms that persist for more than 6 weeks, often coming and going over time.
Yes, non-sedating antihistamines like cetirizine or loratadine are safe for long-term use under medical supervision. They are commonly prescribed for daily symptom control.