


Date: 12 Nov 2025
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a central role in maintaining overall health and wellness. While it is best known for supporting strong bones and calcium absorption, scientific evidence has increasingly linked adequate Vitamin D levels to improved mood and the prevention of chronic conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes.
Despite its importance, Vitamin D deficiency remains widespread, especially in regions with limited sunlight exposure, poor dietary intake, or restricted outdoor activity.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Unlike other vitamins, it can be synthesized by the body when the skin is exposed to direct sunlight, making sunlight one of the primary natural sources. It also exists in two main forms:
Several clinical studies have linked Vitamin D deficiency to depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. This vitamin plays a role in the regulation of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which is involved in mood stabilization. Adequate levels may help reduce symptoms of depression and improve overall emotional well-being.
Low Vitamin D levels have also been associated with seasonal affective disorder (SAD)—a type of depression that occurs during seasons with reduced sunlight exposure. Supplementation, along with safe sun exposure, has been shown to enhance mood and cognitive function.
Emerging research suggests that Vitamin D may have a protective effect against certain cancers, particularly colon, breast, and prostate cancers. Its active form, calcitriol, is believed to slow cancer cell growth, promote cell differentiation, and reduce inflammation—all processes critical in reducing cancer risk.
While Vitamin D should not be used as a substitute for cancer treatment, maintaining optimal levels may serve as a preventive measure when combined with a balanced diet and regular health screenings.
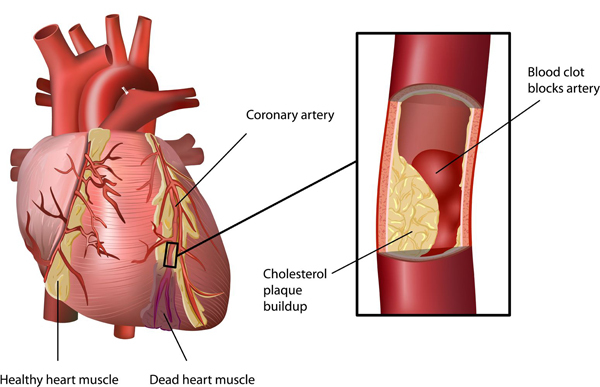
Vitamin D is increasingly recognized for its role in cardiovascular health. Studies suggest that insufficient levels of the vitamin are associated with increased risks of:
The mechanisms involve Vitamin D’s ability to regulate blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and influence calcium metabolism in the arteries. Ensuring sufficient levels may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and support overall heart function.
Vitamin D supports pancreatic function and enhances the body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it a valuable nutrient in the management and prevention of type 2 diabetes. Research shows that individuals with higher Vitamin D levels are less likely to develop insulin resistance—a major precursor to diabetes.
Supplementation may also improve glycemic control in people already diagnosed with diabetes, especially when combined with a healthy diet and physical activity.
Certain groups are at increased risk for Vitamin D deficiency, including:
The recommended daily intake varies depending on age and health status.
Higher doses may be required for those with diagnosed deficiencies, under a healthcare provider's supervision.
Several effective and safe Vitamin D supplements are available to support health and wellness. Here are top options available at Pharmily:
These softgels provide a daily dose of high-potency Vitamin D3 to support immune health, bone strength, and emotional balance. It is ideal for daily maintenance and prevention of deficiency.
Best suited for individuals with severe deficiency or higher requirements, this supplement provides a potent dosage to rapidly restore healthy blood levels under medical guidance.
A comprehensive formula that includes Vitamin D along with other essential vitamins and minerals designed to support women's overall health, hormonal balance, and immunity.
These capsules are a rich natural source of Vitamin D and A, making them effective in boosting immune function and maintaining healthy bones and joints.
While supplements are useful, moderate sun exposure remains one of the most effective natural ways to increase Vitamin D levels. Just 10–30 minutes of sunlight a few times a week can help, depending on skin tone and weather.
Dietary sources include:
Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in not only maintaining skeletal health but also in enhancing mood, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and supporting the immune system. Addressing Vitamin D deficiency through safe sun exposure, dietary intake, and high-quality supplements—such as those available at Pharmily—can offer long-term protective health benefits.
Regular screening and supplementation, especially for at-risk groups, should be considered part of any preventive health strategy. By investing in this essential nutrient, individuals can significantly enhance their quality of life and reduce their vulnerability to serious health conditions.
1. How do I know if I have a Vitamin D deficiency?
Common signs include fatigue, low mood, muscle weakness, and frequent illnesses. A simple blood test can confirm your Vitamin D levels.
2. Can I get enough Vitamin D from sunlight alone?
In most cases, moderate sun exposure provides adequate Vitamin D, but factors like skin tone, sunscreen use, and climate can affect synthesis — making supplementation beneficial for many people.
3. Are there risks to taking too much Vitamin D?
Yes. Excessive Vitamin D intake can lead to toxicity, causing high calcium levels, nausea, and kidney issues. Always follow recommended doses or consult your healthcare provider.
4. Which form of Vitamin D is better — D2 or D3?
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is the preferred and more effective form for maintaining healthy Vitamin D levels in the body.