

Date: 12 Nov 2025
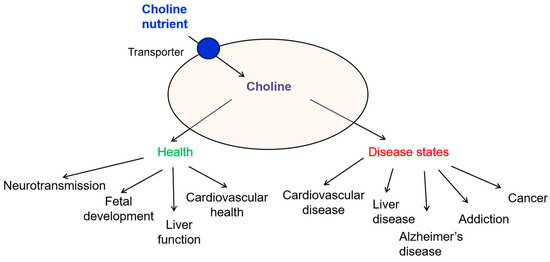
Choline is an essential nutrient vital for liver function, brain development, nerve signaling, and fat metabolism. Deficiency in choline may lead to a health condition often referred to as choline disease, which is marked by liver damage, cognitive impairment, and in some cases, pancreatic disorders.
Although not formally classified as a standalone disease in medical literature, choline deficiency syndrome is increasingly recognized as a serious metabolic concern that contributes to various organ dysfunctions.
Choline is a water-soluble compound that functions similarly to B vitamins. It plays a key role in:
Since the body produces only a small amount of choline, most of it must be obtained through diet or supplementation.

Choline deficiency can disrupt several metabolic processes, resulting in the onset of "choline disease." This condition may manifest through various clinical symptoms, including:
1. Fatty Liver (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease - NAFLD)
When choline levels are inadequate, the liver struggles to metabolize fats efficiently, causing lipid accumulation in hepatic tissues.
2. Pancreatic Dysfunction
Emerging studies suggest that choline deficiency may impair insulin secretion and glucose regulation, placing individuals at higher risk of metabolic syndromes.
3. Neurological Impairment
Choline is critical for producing acetylcholine, which supports memory, muscle control, and mood regulation. Deficiency may contribute to memory loss, cognitive decline, and even mood disorders.
Several factors may contribute to a lack of adequate choline in the body:
Choline deficiency may affect individuals from various backgrounds, but certain groups are more vulnerable, including:
While there is no standardized blood test for choline, diagnosis often involves:
Preventing choline disease involves ensuring adequate choline intake through dietary sources such as eggs, beef liver, salmon, soybeans, and broccoli. However, in cases where dietary choline is insufficient, supplementation becomes essential.

Pharmily Kenya provides effective choline-based supplements that support liver health, brain function, and overall metabolic balance. Below are top pharmacist-recommended options:
This dual-action supplement combines choline and inositol, two powerful lipotropic agents that promote fat metabolism and liver detoxification. Regular intake supports neural communication and may reduce fatty liver risk.
Alpha GPC is a highly bioavailable form of choline that efficiently crosses the blood-brain barrier. It directly contributes to acetylcholine production, making it ideal for enhancing cognitive performance, memory, and mood regulation.
Derived from lecithin, phosphatidyl choline supports cell membrane integrity and liver regeneration. It plays a vital role in emulsifying fats, thereby aiding digestion and preventing fatty liver buildup.
Additional Preventive Tips
Although choline disease is often underdiagnosed, its health implications are far-reaching. Left unmanaged, choline deficiency can lead to irreversible liver damage, cognitive decline, and other metabolic disturbances. Prevention and early intervention through diet, lifestyle changes, and supplementation are critical.
Thanks to reliable solutions such as Solgar Choline/Inositol, NOW Alpha GPC, and Phosphatidyl Choline—all available at Pharmily Kenya—managing and preventing choline-related disorders is now more accessible than ever.
1. What are the early signs of choline deficiency?
Early signs of choline deficiency may include fatigue, poor memory, mood swings, and mild liver discomfort. As deficiency progresses, it can lead to fatty liver disease, muscle weakness, and cognitive decline due to reduced acetylcholine production.
2. Can choline deficiency cause permanent damage?
Yes. Long-term choline deficiency can cause lasting liver damage and cognitive impairment if left untreated. However, early intervention with dietary improvements and supplements such as Solgar Choline/Inositol or NOW Alpha GPC can help reverse these effects.
3. What foods are naturally high in choline?
Top choline-rich foods include eggs, beef liver, salmon, soybeans, broccoli, chicken, and cauliflower. These foods help maintain optimal liver and brain health, especially when consumed regularly as part of a balanced diet.
4. Are choline supplements safe for daily use?
When taken as recommended, choline supplements are generally safe and well-tolerated. Always follow dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional before combining supplements, particularly if you have liver conditions or are pregnant.